Photo: Kimmo Ohtonen
Achievements and lessons learnt
The Biodiversity Pilot Programme provided Nefco and the pilot companies with the knowledge and tools to continue integrating biodiversity work into their businesses. As the programme progressed, the work plan also evolved in response to emerging learnings and insights.
Initially, the pilot companies focused on testing and developing solutions to achieve direct, on-the-ground biodiversity improvements. As the companies became more aware of their impacts and dependencies, their focus shifted towards results and outcomes in their work plans and management plans, aligning with long-term biodiversity commitments.
Lessons learnt working with pilot companies
The level of understanding and ambition for biodiversity knowledge and management varied among the pilot companies. However, all the companies made significant progress during the programme in developing the foundation for a business strategy that takes biodiversity into account and integrates it into their business models.
Company-specific key achievements include the following:
BaltCap
- Assigned a specialised biodiversity champion and hired an ESG manager in 2024
- Established biodiversity KPIs and a threshold for guiding future investments
- Decided to integrate biodiversity impact data into its investment process
- Started advocating for biodiversity work in various stakeholder events
Klappir
- Started building biodiversity data based on the European Sustainability Reporting Standard
- Used pilot programme materials to reach out to customers
- Selected energy and maritime companies to pilot the inclusion of biodiversity data
- Aims to test with a few clients in 2024 and scale up to a larger customer base in 2025
Meriaura Energy
- Created a biodiversity checklist for solar heating systems covering sales, system design, project execution and decommissioning
- Found that the programme created competitive value and plans to scale up its learnings in maritime operations
- Included biodiversity in the Sustainability section of its website, social media content and company presentations
- Compiled a list of internal actions taken and showcased biodiversity examples
Norsepower
- Sent an ESG (incl. biodiversity) query to suppliers
- Established local partnerships for biodiversity in China
- Had a Biodiversity Management Plan approved by the management
- Created a group-level ESG Roadmap and established a sustainability task force
Pure Waste Textiles
- Used results from the pilot programme to prioritise efforts and set targets
- Aims to start co-operating with an NGO at its manufacturing site in India to work on biodiversity projects
- Started planning a water conservation initiative and a native plantation and wildlife habitat
Sulapac
- Set a biodiversity action plan with short- and long-term targets
- Identified high-impact areas, such as moving away from virgin feedstock
- Plans to showcase circularity, e.g. a closed-loop project, at the Slush conference
- Designated a dedicated individual for sustainability
“One crucial discovery is that an understanding of biodiversity is essential before advancing any initiatives within a company.”
Key findings formed around risk assessment results, strategy development and biodiversity opportunities
The key findings of the programme are based on the outcomes of the risk assessments, strategic development, and biodiversity opportunities in small and medium-sized companies. One crucial discovery is that creating an understanding of biodiversity is essential before advancing any initiatives within a company. Additionally, integrating biodiversity considerations can bring numerous benefits, including gaining a competitive edge and enhancing corporate reputation through effective communication.
 | These pilot projects will serve as examples for biodiversity work among SMEs, addressing a current gap where most illustrative examples often come from larger companies. |
 | The circular economy reduces biodiversity impacts from business activities/production, but it may be difficult to prove the benefits and effectiveness. |
 | A lot of understanding is needed before biodiversity work can be promoted in a company. This underlines the importance of training and skills. |
 | Biodiversity aspects should be considered already at the planning stage, when it is easiest to minimise the negative impacts of a project and to create positive impacts. |
 | A step-by-step approach and deepening the work process over time makes planning easier and "reduces the pain of the job". |
 | Taking care of biodiversity can become a critical selling point and it can become a competitive advantage compared to other actors. |
 | Value chain analysis has become increasingly important. If the work is done properly, it improves supply chain transparency, which can reduce potential risks to biodiversity impacts and dependencies. |
 | Developing suitable measures to act upon nature-related risks and opportunities creates a strong narrative which can be used for public communications and improves the business reputation. |
 | Biodiversity impacts are often very local. Site-specific analysis is important and provides a good basis for the design, implementation and monitoring of measures. The role of local actors is essential. |
 | Working with different sectors gives a broad range of opportunities in which biodiversity-friendly actions can be implemented and from which all participants can learn. |
Lessons learnt from Nefco’s operations
The portfolio screening provided Nefco with important initial information on the impacts and dependencies of its investments in nature. Based on the screening results, potential high-risk portfolio sectors and projects were identified. This information was used to develop the building blocks of the Biodiversity Roadmap and key actions for Nefco.
Nefco and the pilot companies have also continued to share the programme's experiences and concrete implementation actions through social media and websites. This ongoing communication has contributed to scaling up results and lessons learnt, thereby inspiring others with practical examples.

Photo: Meriaura Energy
Level of understanding and knowledge sharing
Until now, global biodiversity and nature conservation efforts have mostly been led by governments, policymakers, NGOs and academia. Directly involving the private and financial sectors in biodiversity management by mitigating risks, creating positive impacts, and promoting financing opportunities is crucial to closing the significant financial gap needed to halt nature loss. The key success of the Biodiversity Pilot Programme is its initiation of dialogue between key players in global biodiversity conservation and the private and financial sectors.
Through this programme, Nefco has successfully created an environment for engaging with SMEs on biodiversity issues. The participating companies already have a strong sustainability mindset, making them more receptive to these new challenges. Despite their existing knowledge, they face difficulties in fully understanding the issue. Additionally, the abundance of information on biodiversity may be a hurdle in getting more companies on board in the future.
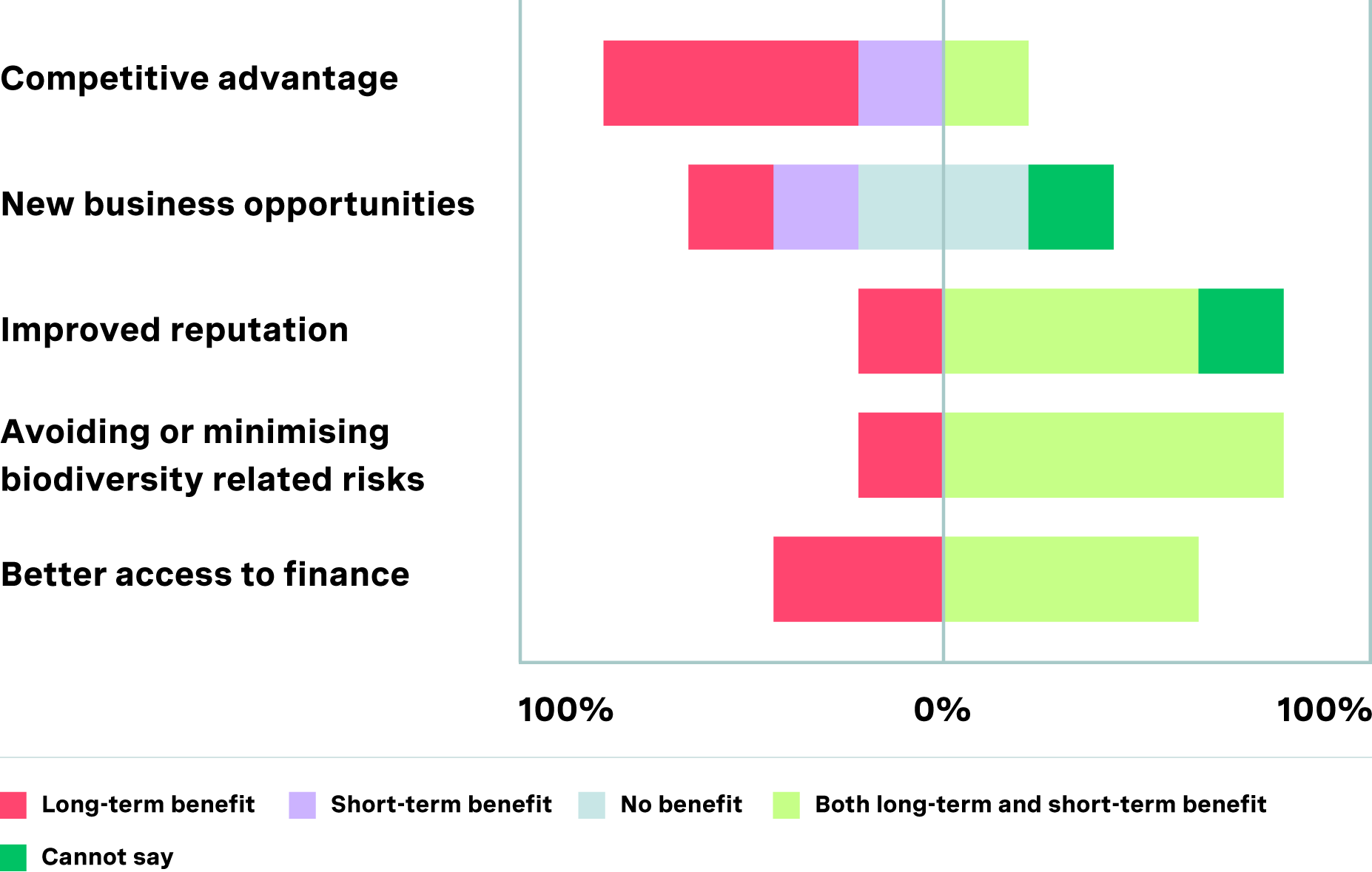
Overall, the participating companies were very satisfied with the programme, giving the experience an average rating of 4.4 out of 5. They perceived various benefits, including competitive advantage, new business opportunities, improved reputation, avoidance or minimisation of biodiversity-related risks, and better access to finance. However, there were differences in whether the companies viewed these as short or long-term benefits.
Perception of different business benefits gained
from the Biodiversity Pilot Programme
 |
4.4/5
Average rating given to the programme by participating companies
“Through this programme, Nefco has successfully created an environment for engaging with SMEs on biodiversity issues.”